e-Newsletter January 2024
Our monthly e-Newsletter featuring the latest updates from Retina UK. Subscribe now to receive these updates directly to your email.
Search results
Our monthly e-Newsletter featuring the latest updates from Retina UK. Subscribe now to receive these updates directly to your email.
Our monthly e-Newsletter featuring the latest updates from Retina UK. Subscribe now to receive these updates directly to your email.
Our monthly e-Newsletter featuring the latest updates from Retina UK. Subscribe now to receive these updates directly to your email.
Our monthly e-Newsletter featuring the latest updates from Retina UK. Subscribe now to receive these updates directly to your email.
From our newsletters to the recordings of our webinars and everything in-between, use the filters (below) to find the content that's right for you.
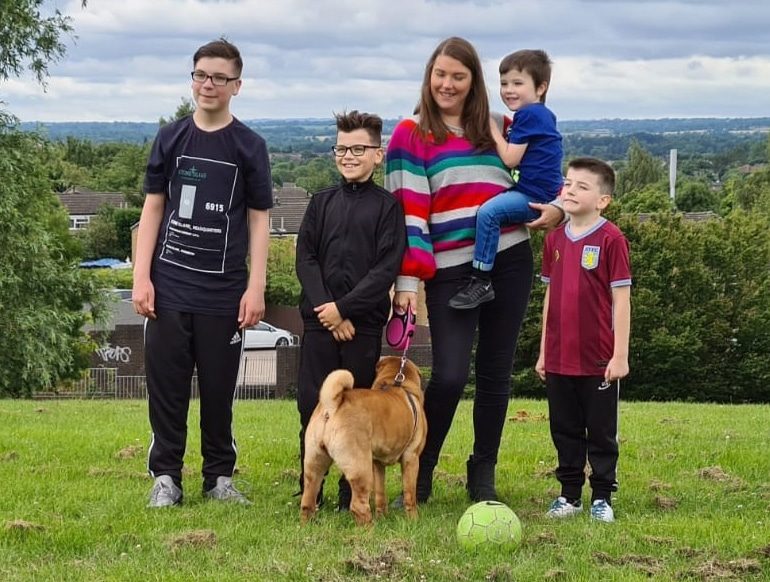

Different inherited sight loss conditions present noticeable symptoms at different times.
Biotechnology company Kiora Pharmaceuticals has been given the go-ahead to start in-human testing of a novel “small molecule” treatment, known as KIO-301, for advanced vision loss in retinitis pigmentosa (RP). The phase 1b clinical trial will take place in Adelaide, Australia, and will begin enrolling participants towards the end of 2022.

This edition includes exciting news about our Annual and Professionals’ Conferences. We hope as many of you as possible can join us in Manchester, or online, in September. You’ll also find updates about the latest research and a feature on one of our funded researchers, Dr Jörn Lakowski.
In recent years there has, understandably, been a lot of excitement around cutting-edge therapies that target the specific genetic faults underlying inherited sight loss.
Progress towards treatments for inherited retinal conditions continues to gather pace and there’s been lots going on in the last few months, with more and more approaches being explored. This round-up gives a flavour of the variety of developments, including plenty that are not specific to a particular genetic fault.